Magnetic Resonance Imaging sebagai Penegak Diagnosa Cervical Radioculopathy
Cervical adalah tulang pembentuk kerangka pada leher. Ukurannya yang lebih kecil memperlihatkan fakta bahwa cervical menanggung beban lebih sedikit dibandingkan dengan vertebra inferior yang lebih besar. Meskipun diskus IV cervical lebih tipis daripada diskus inferior, diskus tersebut relatif lebih tebal dibandingkan ukuran corpus vertebra yang tersambung dengannya. Ketebalan dari diskus IV, dekat dengan orientasi horizontal dari articular facets, dan sejumlah dari massa tubuh di sekitarnya memberikan daerah cervical kemudahan dan memiliki kemampuan dalam bergerak lebih bebas dari vertebra yang lain <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"ISSN":"00987484","abstract":"\"Clinically Oriented Anatomy provides first-year medical students with the clinically oriented anatomical information as it relates to the practice of medicine, dentistry, and physical therapy. The 7th edition features a fully revised art program to ensure consistency and cohesiveness of imaging style\"--Provided by publisher.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Moore, K. L.; Dalley, A. F.; Agur","given":"A. M. R.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Wolters Kluwer","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"15","issued":{"date-parts":[["2014"]]},"title":"Moore Clinically Oriented Anatomy Seventh Edition","type":"book","volume":"282"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=e23246cb-eb64-364c-b2e9-04411cf59be8"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Moore, K. L.; Dalley, A. F.; Agur, 2014)","manualFormatting":"(Moore, 2014)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Moore, K. L.; Dalley, A. F.; Agur, 2014)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Moore, K. L.; Dalley, A. F.; Agur, 2014)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Moore, 2014)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Salah satu kelainan yang dapat terjadi pada cervical adalah Radiculopathy. Radiculopathy yaitu keadaan yang berhubungan dengan gangguan fungsi dan struktur akar saraf sebagai akibat dari proses patologi yang mengenai satu atau lebih dari akar saraf dengan pola gangguan yang bersifat dermatomal. Radiculopathy merupakan salah satu patologis dari cervical root syndrome<!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"ISBN":"6103544947","abstract":"Kinerja Keuangan Daerah, Belanja Modal, dan Pertumbuhan Ekonomi. vii","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Nahadewa","given":"Tjokorda Gde Bagus","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"PT. Indeks","id":"ITEM-1","issued":{"date-parts":[["2013"]]},"page":"1-61","title":"Saraf Perifer","type":"article-journal"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=b1b9d2c9-19ef-4760-8c8f-5fabefbffd62"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Nahadewa, 2013)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Nahadewa, 2013)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Nahadewa, 2013)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Nahadewa, 2013)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Adanya rasa nyeri yang menjalar merupakan manifestasi klinis radiculopathy <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"ISSN":"1718-4304","abstract":"INTRODUCTION: Little is known regarding the causes and outcomes of peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU). We explored the outcomes of technique failure and mortality in a cohort of PD patients admitted to the ICU.\\n\\nMETHODS: Using a provincial database of 990 incident PD patients followed from January 1997 to June 2009, we identified 90 (9%) who were admitted to the ICU. Parametric and nonparametric tests were used as appropriate to determine differences in baseline characteristics. The Cox proportional hazards and competing risk methods were used to investigate associations.\\n\\nRESULTS: Compared with other patients, those admitted to the ICU had been on PD longer (p < 0 xss=removed uuid=c49891af-f2a2-3580-b11c-ef5a3cb646d4 xss=removed><![endif]-->(Maksum, dkk, 2016)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Cervical radiculopathy merupakan klinis yang umum. Terjadi karena kompresi di radiks saraf cervical. Cervical radiculopathy adalah nyeri atau sindrom defisit sensorimotor yang di artikan akibat dari kompresi akar saraf cervical. Kompresi itu sendiri dapat terjadi sebagai akibat herniasi diskus, degenerative disease, spondylosis, tumor, trauma, stenosis, cervical root syndrome. Pasien dapat mengeluh dari nyeri,mati rasa, kesemutan di ekstremitas atas <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1007/s11420-011-9218-z","ISSN":"15563316","abstract":"Background: Cervical radiculopathy is defined as a syndrome of pain and/or sensorimotor deficits due to compression of a cervical nerve root. Understanding of this disease is vital for rapid diagnosis and treatment of patients with this condition, facilitating their recovery and return to regular activity. Purpose: This review is designed to clarify (1) the pathophysiology that leads to nerve root compression; (2) the diagnosis of the disease guided by history, physical exam, imaging, and electrophysiology; and (3) operative and non-operative options for treatment and how these should be applied. Methods: The PubMed database was searched for relevant articles and these articles were reviewed by independent authors. The conclusions are presented in this manuscript. Results: Facet joint spondylosis and herniation of the intervertebral disc are the most common causes of nerve root compression. The clinical consequence of radiculopathy is arm pain or paresthesias in the dermatomal distribution of the affected nerve and may or may not be associated with neck pain and motor weakness. Patient history and clinical examination are important for diagnosis. Further imaging modalities, such as x-ray, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and electrophysiologic testing, are of importance. Most patients will significantly improve from non-surgical active and passive therapies. Indicated for surgery are patients with clinically significant motor deficits, debilitating pain that is resistant to conservative modalities and/or time, or instability in the setting of disabling radiculopathy. Surgical treatment options include anterior cervical decompression with fusion and posterior cervical laminoforaminotomy. Conclusion: Understanding the pathophysiology, diagnosis, treatment indications, and treatment techniques is essential for rapid diagnosis and care of patients with cervical radiculopathy. © 2011 Hospital for Special Surgery.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Caridi","given":"John M.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Pumberger","given":"Matthias","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Hughes","given":"Alexander P.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"HSS Journal","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"3","issued":{"date-parts":[["2011"]]},"page":"265-272","title":"Cervical Radiculopathy: A Review","type":"article-journal","volume":"7"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=1dc6f5a0-e85f-48d5-91df-fdbed3a54876"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Caridi et al., 2011)","manualFormatting":"(Caridi dkk, 2011)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Caridi et al., 2011)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Caridi et al., 2011)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Caridi dkk, 2011)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Kompresi radiks saraf cervical bisa terjadi karena herniasi diskus atau osteofit tulang yang telah menimpa radiks saraf cervical <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1007/s12178-016-9349-4","ISSN":"19359748","abstract":"Cervical radiculopathy is a common clinical scenario. Patients with radiculopathy typically present with neck pain, arm pain, or both. We review the epidemiology of cervical radiculopathy and discuss the diagnosis of this condition. This includes an overview of the pertinent findings on the patient history and physical examination. We also discuss relevant clinical syndromes that must be considered in the differential diagnosis including peripheral nerve entrapment syndromes and shoulder pathology. The natural history of cervical radiculopathy is reviewed and options for management are discussed. These options include conservative management, non-operative modalities such as physical therapy, steroid injections, and operative intervention. While the exact indications for surgical intervention have not yet been elucidated, we provide an overview of the available literature regarding indications and discuss the timing of intervention. The surgical outcomes of anterior cervical decompression and fusion (ACDF), cervical disc arthroplasty (CDA), and posterior cervical foraminotomy (PCF) are discussed.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Iyer","given":"Sravisht","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Kim","given":"Han Jo","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"3","issued":{"date-parts":[["2016"]]},"title":"Cervical radiculopathy","type":"article","volume":"9"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=de99eb46-b293-3dfd-ad72-4c983f7494ee"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Iyer & Kim, 2016)","manualFormatting":"(Iyer dan Kim, 2016)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Iyer & Kim, 2016)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Iyer & Kim, 2016)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Iyer dan Kim, 2016)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. faktor resiko yang banyak di ketahui yaitu mengangkat beban berat, menyelam, dan bermain golf. 30% pasien telah melaporkan radiculopathy menimbulkan nyeri saat duduk, berjalan, dan berdiri <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1007/s12178-016-9349-4","ISSN":"19359748","abstract":"Cervical radiculopathy is a common clinical scenario. Patients with radiculopathy typically present with neck pain, arm pain, or both. We review the epidemiology of cervical radiculopathy and discuss the diagnosis of this condition. This includes an overview of the pertinent findings on the patient history and physical examination. We also discuss relevant clinical syndromes that must be considered in the differential diagnosis including peripheral nerve entrapment syndromes and shoulder pathology. The natural history of cervical radiculopathy is reviewed and options for management are discussed. These options include conservative management, non-operative modalities such as physical therapy, steroid injections, and operative intervention. While the exact indications for surgical intervention have not yet been elucidated, we provide an overview of the available literature regarding indications and discuss the timing of intervention. The surgical outcomes of anterior cervical decompression and fusion (ACDF), cervical disc arthroplasty (CDA), and posterior cervical foraminotomy (PCF) are discussed.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Iyer","given":"Sravisht","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Kim","given":"Han Jo","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"3","issued":{"date-parts":[["2016"]]},"title":"Cervical radiculopathy","type":"article","volume":"9"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=de99eb46-b293-3dfd-ad72-4c983f7494ee"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Iyer & Kim, 2016)","manualFormatting":"(Iyer dan Kim, 2016)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Iyer & Kim, 2016)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Iyer & Kim, 2016)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Iyer dan Kim, 2016)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Modalitas yang dapat digunakan untuk memperlihatkan radiculopathy antara lain computed tomography (CT) Scan dan Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). CT scan mampu menampakkan kelainan tulang tetapi kurang untuk menilai kanalis spinalis. Sedangkan MRI berguna untuk memperlihatkan diskus, medula spinalis dan radiks saraf di daerah cervical yang mungkin tidak terlihat pada CT scan <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"abstract":"This chapter discusses the issue of restoration of ecosystem function versus species diversity. Although the two goals are not mutually exclusive, the balance between the two approaches depends on the explicit goal of restoration. Restoration of a self-sustaining ecosystem may require a fair amount of biodiversity. Restoration of ecosystem function may require simplification of ecosystems by classifying species into functional groups. Functional and compositional diversity are compared and related to the concept of ecological redundancy. Data are presented where species which initially appear to be functionally equivalent respond very differently to episodic environmental variability. The following points are made. (1) Preservation of diversity cannot occur in the absence of functioning ecosystems. (2) Biodiversity plays a significant role in sustaining ecosystem function. (3) Keystone species can be defined only in the context of a specific ecosystem function, and may vary spatially and temporally. (4) Ecological redundancy should be viewed in the context of long-term environmental variation.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Panduwinata","given":"Widya","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Cdk","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"4","issued":{"date-parts":[["2014"]]},"title":"Peranan Magnetic Resonance Imaging dalam Diagnosis Nyeri Punggung Bawah Kronik","type":"article-journal","volume":"41"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=819363a7-369c-38fc-a517-4b9fc71b4394"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Panduwinata, 2014)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Panduwinata, 2014)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Panduwinata, 2014)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Panduwinata, 2014)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) menjadi peran penting pada yang berhubungan dengan radiculopathy atau stenosis tulang belakang dan nyeri punggung. Batas yang lebih jelas dari jaringan lunak di tulang belakang menjadikan MRI modalitas penggambaran yang disukai <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1007/s00586-011-2019-8","ISBN":"0058601120","ISSN":"09406719","PMID":"21922287","abstract":"Purpose In about 5% of all cases LBP is associated with serious underlying pathology requiring diagnostic confirmation and directed treatment. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is often used for this diagnostic purpose yet its role remains controversial. Consequently, this review aimed to summarize the available evidence on the diagnostic accuracy of MRI for identifying lumbar spinal pathology in adult low back pain (LPB) or sciatica patients. Methods MEDLINE, EMBASE and CINAHL were searched (until December 2009) for observational studies assessing the diagnostic accuracy of MRI compared to a reference test for the identification of lumbar spinal pathology. Two reviewers independently selected studies for inclusion, extracted data and assessed methodological quality. Pooled summary estimates of sensitivity and specificity with 95% confidence intervals were calculated for homogenous subsets of studies. Results Eight studies were included in this review. Strata were defined for separate pathologies i.e. lumbar disc herniation (HNP) and spinal stenosis. Five studies comparing MRI to findings at the surgery for identifying HNP were included in a meta-analysis. Pooled analysis resulted in a summary estimate of sensitivity of 75% (95% CI 65-83%) and specificity of 77% (95% CI 61-88%). For spinal stenosis pooling was not possible. Conclusions The results suggest that a considerable proportion of patients may be classified incorrectly by MRI for HNP and spinal stenosis. However, the evidence for the diagnostic accuracy of MRI found by this review is not conclusive, since the results could be distorted due to the limited number of studies and large heterogeneity. © 2011 Springer-Verlag.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Wassenaar","given":"Merel","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Rijn","given":"Rogier M.","non-dropping-particle":"Van","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Tulder","given":"Maurits W.","non-dropping-particle":"Van","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Verhagen","given":"Arianne P.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Windt","given":"Danielle A.W.M.","non-dropping-particle":"Van Der","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Koes","given":"Bart W.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Boer","given":"Michiel R.","non-dropping-particle":"De","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Ginai","given":"Abida Z.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Ostelo","given":"Raymond W.J.G.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"European Spine Journal","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"2","issued":{"date-parts":[["2012"]]},"page":"220-227","title":"Magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing lumbar spinal pathology in adult patients with low back pain or sciatica: A diagnostic systematic review","type":"article-journal","volume":"21"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=27b0b4e8-1b5e-475d-ac43-befbdaa749df"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Wassenaar et al., 2012)","manualFormatting":"(Wassenaar, dkk, 2012)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Wassenaar et al., 2012)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Wassenaar et al., 2012)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Wassenaar, dkk, 2012)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Meskipun Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) merupakan salah satu teknologi terbarukan dalam mendiagnosa kelainan pada tulang belakang, akan tetapi dalam penggambaran tulang belakang masih terdapat beberapa kesulitan karena struktur anatomi yang kompleks dan berbagai artefak. Nyeri yang dirasakan, usia, dan kondisi umum lainnya seperti gerakan menelan,bernafas,dan pergerakan CSF yang cepat sering menjadi penyebab terganggunya kualitas gambar <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1055/s-0033-1350346","ISSN":"14389029","PMID":"23999783","abstract":"Purpose: Using the BLADE (PROPELLER) technique for T2-weighted MR imaging of the cervical spine has proven to be a reliable tool for reducing artifacts typically for this region. The aim of this study was to evaluate whether the application of BLADE sequences has an impact on the detection of small or low contrast spinal cord and epidural lesions. Materials and Methods: A standard TSE and a BLADE sequence were compared in 33 patients with 46 spinal cord and epidural lesions for T2-weighted sagittal imaging of the cervical spine. Image sharpness, visualization of the dura, reliability of spinal cord depiction as well as lesion contrast were evaluated by two independent readers. Additionally two experienced neuroradiologists selected in consensus the sequence they would prefer for diagnostic purposes. Statistical evaluations were performed using the sign and the ?2 test. Results: BLADE was significantly superior to TSE regarding image sharpness, visualization of the dura and reliability of spinal cord depiction. Regarding lesion contrast there was a positive trend towards the BLADE sequence. In 17 of 46 lesions, BLADE was judged superior to TSE, while TSE was favored in 10 lesions. In consensus reading both neuroradiologists preferred BLADE for overall image quality in 27 of 33 patients and for lesion contrast in 10 and TSE in 14 of the 33 patients, but 3 TSE sequences were rated as non-diagnostic regarding this criterion. Conclusion: For the detection of even small and low-contrast spinal cord lesions, BLADE is at least equivalent to TSE, yielding better overall image quality and fewer non-diagnostic images. © 2013 Georg Thieme Verlag KG Stuttgart New York.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Finkenzeller","given":"T.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Menzel","given":"C.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Fellner","given":"F. A.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Fellner","given":"C. W.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Stroszczynski","given":"C.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Schuierer","given":"G.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Fellner","given":"C.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"RoFo Fortschritte auf dem Gebiet der Rontgenstrahlen und der Bildgebenden Verfahren","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"1","issued":{"date-parts":[["2014"]]},"page":"47-53","title":"BLADE sequences in sagittal T2-weighted MR imaging of the cervical spine and spinal cord - Lesion detection and clinical value","type":"article-journal","volume":"186"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=b58783d8-ca91-4b7f-98c9-41082ad2322e"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Finkenzeller et al., 2014)","manualFormatting":"(Finkenzeller, dkk, 2014)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Finkenzeller et al., 2014)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Finkenzeller et al., 2014)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Finkenzeller, dkk, 2014)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Bila penyakit sudah stadium lanjut seperti tumor primer, metastasis, degenerasi, nyeri saat menjalani pemeriksaan MRI pasien sering mengalami rasa sakit yang dapat mengurangi tingkat kooperatif pasien dan pergerakan yang tidak diinginkan <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1016/j.mri.2013.03.006","ISSN":"0730725X","abstract":"The purpose of this study is to evaluate the ability of T2 turbo spin echo (TSE) axial and sagittal BLADE sequences in reducing or even eliminating motion, pulsatile flow and cross-talk artifacts in lumbar spine MRI examinations. Forty four patients, who had routinely undergone a lumbar spine examination, participated in the study. The following pairs of sequences with and without BLADE were compared: a) T2 TSE Sagittal (SAG) in thirty two cases, and b) T2 TSE Axial (AX) also in thirty two cases. Both quantitative and qualitative analyses were performed based on measurements in different normal anatomical structures and examination of seven characteristics, respectively. The qualitative analysis was performed by experienced radiologists. Also, the presence of image motion, pulsatile flow and cross-talk artifacts was evaluated. Based on the results of the qualitative analysis for the different sequences and anatomical structures, the BLADE sequences were found to be significantly superior to the conventional ones in all the cases. The BLADE sequences eliminated the motion artifacts in all the cases. In our results, it was found that in the examined sequences (sagittal and axial) the differences between the BLADE and conventional sequences regarding the elimination of motion, pulsatile flow and cross-talk artifacts were statistically significant. In all the comparisons, the T2 TSE BLADE sequences were significantly superior to the corresponding conventional sequences regarding the classification of their image quality. In conclusion, this technique appears to be capable of potentially eliminating motion, pulsatile flow and cross-talk artifacts in lumbar spine MR images and producing high quality images in collaborative and non-collaborative patients. © 2013 Elsevier Inc.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Lavdas","given":"Eleftherios","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Mavroidis","given":"Panayiotis","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Kostopoulos","given":"Spiros","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Glotsos","given":"Dimitrios","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Roka","given":"Violeta","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Koutsiaris","given":"Aristotle G.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Batsikas","given":"Georgios","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Sakkas","given":"Georgios K.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Tsagkalis","given":"Antonios","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Notaras","given":"Ioannis","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Stathakis","given":"Sotirios","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Papanikolaou","given":"Nikos","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Vassiou","given":"Katerina","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Magnetic Resonance Imaging","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"6","issued":{"date-parts":[["2013"]]},"title":"Elimination of motion, pulsatile flow and cross-talk artifacts using blade sequences in lumbar spine MR imaging","type":"article-journal","volume":"31"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=1d116683-9219-36d3-8991-174c3d758631"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Lavdas, Mavroidis, Kostopoulos, et al., 2013)","manualFormatting":"(Lavdas, dkk, 2013)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Lavdas, Mavroidis, Kostopoulos, et al., 2013)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Lavdas, Mavroidis, Kostopoulos, et al., 2013)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Lavdas, dkk, 2013)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Pencitraan magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) cervical dapat dengan mudah menunjukkan perubahan struktural di diskus vertebralis, kanal tulang belakang dan spinal cord. Tetapi anatomi akar saraf cervical rumit dan ramping. Pemilihan sekuen yang tepat selama pemeriksaan dan pencitraan yang jelas dari struktur akar saraf cervical sangat penting <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1097/MD.0000000000024207","ISBN":"0000000000024","ISSN":"15365964","PMID":"33530213","abstract":"Currently, minute structures, such as cervical nerve roots, can be viewed using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) sequences; however, studies comparing multiple sequences in the same set of patients are rare. The aim of the study is to compare the diagnostic values of three 3.0-T MRI sequences used in the imaging of cervical nerve roots. This study included 2 phases. In the first phase (n = 45 patients), the most optimal MRI sequence was determined. In the second phase, this MRI sequence was compared with surgical results (n = 31 patients). The three-dimensional double-echo steady-state (3D-DESS), multi-echo data image combination (MEDIC), and 3D sampling perfection with application-optimized contrasts using different flip angle evolutions (3D-SPACE) sequences were performed to analyze the image quality. Furthermore, the most optimal MRI sequence was compared with surgical results to determine the agreement rate. The image quality scores of the 3 sequences were significantly different (P < .05). The score for 3D-DESS sequence was superior to that of MEDIC sequence, while the score for 3D-SPACE sequence was the worst. For visualization of compressed nerve roots, 3D-DESS sequence was superior to the other 2 sequences in terms of the total quality score and compressed nerve root score. Therefore, 3D-DESS sequence was used for MRI in 31 patients with cervical spondylosis in the second phase of this study. The diagnostic agreement rate was 93.5%. This study concluded that in patients with cervical radiculopathy, the 3D-DESS sequence is superior to the MEDIC and 3D-SPACE sequences and shows a high agreement rate with the surgical diagnosis.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Wang","given":"Qi","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Li","given":"Huixia","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Kong","given":"Jianjun","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Li","given":"Xiaohui","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Feng","given":"Lin","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Wu","given":"Zhanyong","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Medicine (United States)","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"4","issued":{"date-parts":[["2021"]]},"page":"0-5","title":"Diagnostic agreement between 3.0-T MRI sequences of nerve root and surgery in patients with cervical radiculopathy A retrospective study","type":"article-journal","volume":"100"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=ff58fc64-adb9-40c7-95d8-30739f9579e9"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Wang et al., 2021)","manualFormatting":"(Wang dkk, 2021)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Wang et al., 2021)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Wang et al., 2021)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Wang dkk, 2021)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->. Sekuen MRI standar yang digunakan adalah dua dimensi (2D) T1 FSE dan T2, dan T2* Gradien Echo (GRE). Terdapat sekuen baru yang dikembangkan untuk memberikan kontras T2-Weighted yang ditingkatkan seperti 2D Multiple Echo Recombined Gradien Echo (MERGE) <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1002/jmrs.433","ISSN":"20513909","PMID":"32931647","abstract":"Introduction: High-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the cervical spinal cord is important to provide accurate diagnosis and pathological assessment of injuries. MEDIC (Multiple Echo Data Image Combination) sequences have been used in clinical MRI; however, a comparison of the performance of 2D and 3D MEDIC for cervical spinal cord imaging has not been reported. The aim of this study is to compare axial 2D and 3D MEDIC for the visualisation of the grey matter (GM) and white matter (WM) of the human cervical spinal cord. Methods: Eight healthy participants were scanned using Siemens Prismafit 3T MRI. T2*-weighted gradient spoiled 2D and 3D MEDIC sequences were acquired at 0.4 × 0.4 × 3.0 and 0.3 × 0.3 × 3.0 mm resolutions, with the acquisition times of 6 and 7 min, respectively. Quantitative analyses of the images were made based on the image signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) and non-uniformity (NU). Two independent radiologists (CS and FN), each provided Likert scoring assessments of anatomical visibility of the GM and WM structures and image clarity for all samples. Results: Quantitative evaluation showed that 3D MEDIC provided higher SNR, higher CNR and lower NU than 2D MEDIC. However, 2D MEDIC provided better anatomical visibility for the GM, WM and CSF, and higher image clarity (lower artefacts) compared to 3D MEDIC. Conclusions: 2D MEDIC provides better information for depicting the internal structures of the cervical spinal cord compared to 3D MEDIC.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Asiri","given":"Abdullah","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Dimpudus","given":"Franky","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Atcheson","given":"Nicole","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Al-Najjar","given":"Aiman","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"McMahon","given":"Katie","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""},{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Kurniawan","given":"Nyoman D.","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Journal of Medical Radiation Sciences","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"1","issued":{"date-parts":[["2021"]]},"page":"4-12","title":"Comparison between 2D and 3D MEDIC for human cervical spinal cord MRI at 3T","type":"article-journal","volume":"68"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=42087195-ba5c-4165-9909-56cf14eee7af"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Asiri et al., 2021)","manualFormatting":"(Asiri dkk, 2021)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Asiri et al., 2021)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Asiri et al., 2021)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->(Asiri dkk, 2021)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->.
Menurut <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"abstract":"The Handbook of MRI Technique is now an established text for many MRI practitioners around the world. MRI in Practice (also published by Wiley Blackwell) provides radiographers and radiologists with a user-friendly approach to MRI theory and how it may be applied in practice. The book is intended to guide the uninitiated through scanning techniques and protocols and to help more experienced practitioners improve image quality and recognize and rectify common artefacts. In many countries, a lack of educational facilities and funding, as well as the complex nature of the subject, has resulted in practitioners experiencing difficulty in learning MRI techniques. The book has filled this gap and has proven to be a useful clinical text. In this, the fourth edition, it has been my intention to continue with the objectives of previous editions but update the reader on recent advances. Experienced MRI practitioners from the United Kingdom, United States and Europe have made important contributions to reflect these advances and their practice.","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Catherine","given":"Westbrook","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Journal of Experimental Psychology: General","id":"ITEM-1","issue":"1","issued":{"date-parts":[["2014"]]},"title":"Handbook of MRI Technique 4th edition","type":"book","volume":"136"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=60dd89f0-b5a4-3489-b2d3-72cc2bd0f1b8"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Catherine, 2014)","manualFormatting":"Westbrook (2014)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Catherine, 2014)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Catherine, 2014)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->Westbrook (2019)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]--> protokol pemeriksaan MRI Cervical rutin menggunakan sekuen sagital/coronal Spin Echo (SE)/Fast Spin Echo (FSE) T1 atau coherent Gradien Echo (GRE) T2*, sagital Spin Echo(SE)/Fast Spin Echo(FSE) T1, sagital Spin Echo(SE)/Fast Spin Echo (FSE) T2 atau coherent Gradien Echo (GRE) T2*, axial/oblique Spin Echo (SE)/Fast Spin Echo (FSE) T1/T2 or coherent Gradien Echo (GRE) T2*. Dengan sekuen tambahan sagital/axial oblik Spin Echo (SE)/Fast Spin Echo (FSE) T1, sagital Spin Echo (SE)/Fast Spin Echo (FSE) T2 atau Short Tau Inversion Recovery (STIR), 3D coherent/incoherent Gradien Echo (GRE) T2*/T1, sagital Spin Echo (SE)/Fast Spin Echo (FSE) T1 atau fast incoherent Gradient Echo (GRE) T1/Proton Density (PD), 3D Balanced Gradien Echo (BGRE) dan menurut <!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN CSL_CITATION {"citationItems":[{"id":"ITEM-1","itemData":{"DOI":"10.1017/CBO9780511551734.040","ISBN":"9780511551734","ISSN":"1040-8371","PMID":"7945898","abstract":"CLINICAL INDICATIONS MRI has becomeaccepted as the most sensitive imaging modality for the study of spine pathology. Specifically, in the examination of spinal cord trauma, soft tissue injury, and acute intervertebral disc injury, MRI has a higher resolution than any other modality. However, despite optimal visualization of MRIs, it is often not the most appropriate initial imaging study because plain film radiographs and CT scans can provide diagnostic information faster and more cost effectively (1). MRI is indicated in blunt spinal trauma patients with neurological findings suggestive of spinal cord injury without a clear explanation following radiographs and/or CT (2). Emergent MRI of the spine is also generally indicated in the evaluation of spinal cord pathology with signs of myelopathy, radiculopathy, and progressive neurological deficit. Despite these seemingly clear indications, the risk of missing a spinal cord injury makes this decision a major dilemma for physicians. The medical and legal ramifications of restricting diagnostic MRI and failing to diagnose a patient with an unstable spine injury are clearly evident. In contrast, the ubiquitous use of expensive and timeconsuming imaging equipment can inappropriately drive up the cost of medical care and possibly render emergency resources unavailable to other patients. Therefore, it is important to gain as much information as possible fromthe history, physical exam, and preliminary imaging studies to aid the physician’s decision for selecting MRI for potential spinal cord pathology (3).","author":[{"dropping-particle":"","family":"Morrison","given":"William","non-dropping-particle":"","parse-names":false,"suffix":""}],"container-title":"Clinical Emergency Radiology","id":"ITEM-1","issued":{"date-parts":[["2020"]]},"number-of-pages":"538-559","title":"MRI of the spine","type":"book"},"uris":["https://www.mendeley.com/documents/?uuid=cf6a6cbb-3800-4401-a541-88a9e32eaaa8"]}],"mendeley":{"formattedCitation":"(Morrison, 2020)","manualFormatting":"Morrison (2020)","plainTextFormattedCitation":"(Morrison, 2020)","previouslyFormattedCitation":"(Morrison, 2020)"},"properties":{"noteIndex":0},"schema":"https://github.com/citation-style-language/schema/raw/master/csl-citation.json"}<![endif]-->Morrison (2020)<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]--> protokol MRI spine rutin menggunakan sekuen T1-Weighted (mengevaluasi anatomi dan bone marrow), sekuen T2-Weighted (untuk anatomi dan patologi), fat saturation T2W, dan Short Tau Inversion Recovery (STIR).
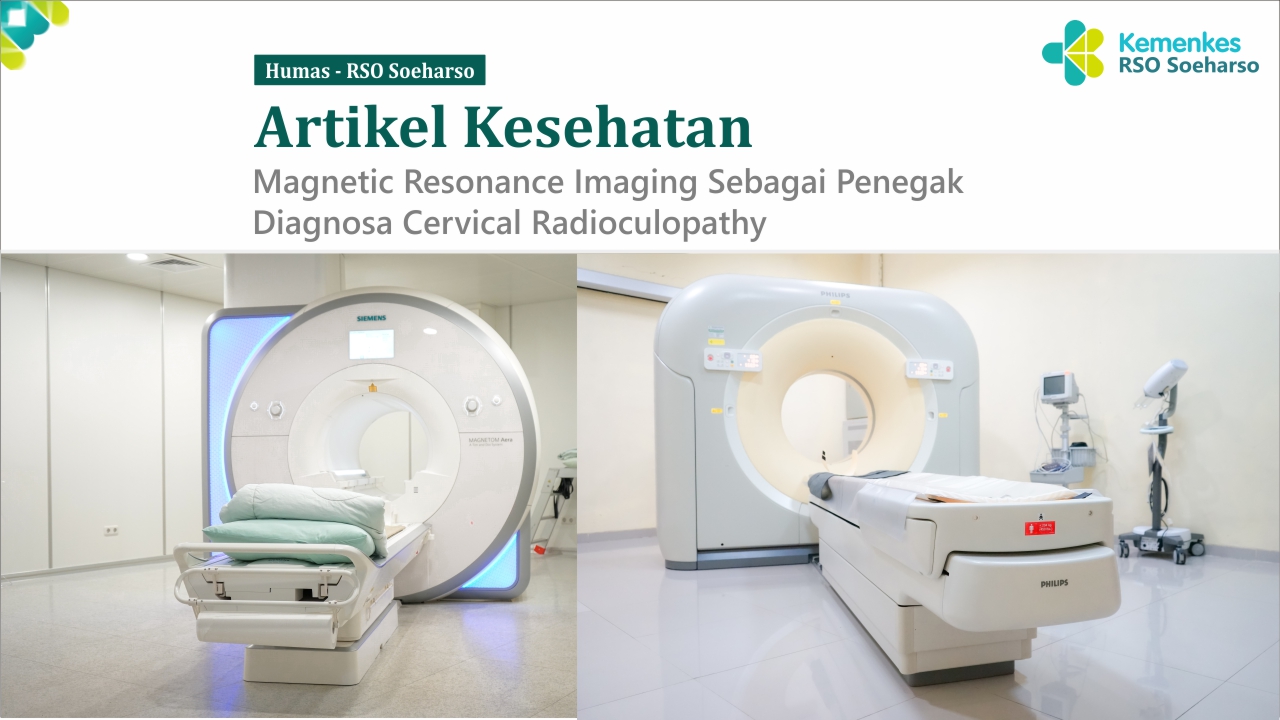
Pemeriksaan MRI cervical dengan diagnosa cervical radioculopathy di RS Ortopedi Prof DR R Soeharso Surakarta, menggunakan modalitas berupa MRI superconductor 1.5 Tesla dengan luas bore magnet 70 cm sehingga pasien akan merasa lebih nyaman dan mengurasi rasa ketakutan pasien pada ruang sempit / claustrophobia dan dilengkapi dengan music yang bisa didengarkan sesuai permintaan pasien untuk meningkatkan kualitas kenyamanan pasien.
Protokol pada pemeriksaan MRI di RS Ortopedi Prof DR R Soeharso Surakarta dilakukan dengan beberapa sequence yaitu dimulai dengan Localizer sebagai mapping awal penentuan lokasi scanning, dilanjutkan dengan pengambilan sequence T2 Fast Spin Echo Sagittal, T1 Spin Echo Sagittal, T2 Fast Spin Echo Coronal, T2 Fast Spin Echo Transversal, T1 Fast Spin Echo Transfersal, dan 3D Myelography. Pada semua sequence kecuali pada 3D myelography diberikan penambahan parameter pre-saturation di area laring faring dengan melakukan blokade pada area yang kemungkinan bisa menyebabkan motion artefak sehingga akan tercipta kualitas gambar yang lebih baik.
Waktu scanning yang diperlukan pemeriksaan MRI cervical di RS Ortopedi Prof DR R Soeharso Surakarta dilakukan kurang dari 30 menit. Sehingga tidak membutuhkan waktu yang tertalu lama, setelah dilakukan pemeriksaan pasien akan mendapatkan hasil berupa QR code untuk mengakses gambar hasil pemeriksaan MRI dan hasil ekspertise MRI secara lengkap dan terupdate, sehingga lebih efisien dan ergonomis dikarenakan hasil yang diarsipka secara digital yang terbarukan.
Referensi :
Asiri, A., Dimpudus, F., Atcheson, N., Al-Najjar, A., McMahon, K., & Kurniawan, N. D. (2021). Comparison between 2D and 3D MEDIC for human cervical spinal cord MRI at 3T. Journal of Medical Radiation Sciences, 68(1), 4–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmrs.433
Finkenzeller, T., Menzel, C., Fellner, F. A., Fellner, C. W., Stroszczynski, C., Schuierer, G., & Fellner, C. (2014). BLADE sequences in sagittal T2-weighted MR imaging of the cervical spine and spinal cord - Lesion detection and clinical value. RoFo Fortschritte Auf Dem Gebiet Der Rontgenstrahlen Und Der Bildgebenden Verfahren, 186(1), 47–53. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0033-1350346
Lavdas, E., Mavroidis, P., Kostopoulos, S., Glotsos, D., Roka, V., Koutsiaris, A. G., Batsikas, G., Sakkas, G. K., Tsagkalis, A., Notaras, I., Stathakis, S., Papanikolaou, N., & Vassiou, K. (2013). Elimination of motion, pulsatile flow and cross-talk artifacts using blade sequences in lumbar spine MR imaging. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 31(6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2013.03.006
Caridi, J. M., Pumberger, M., & Hughes, A. P. (2011). Cervical Radiculopathy: A Review. HSS Journal, 7(3), 265–272. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11420-011-9218-z
Iyer, S., & Kim, H. J. (2016). Cervical radiculopathy. In Current Reviews in Musculoskeletal Medicine (Vol. 9, Issue 3). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12178-016-9349-4
Maksum, M., Hanriko, R., Kedokteran, F., & Lampung, U. (2016). Hernia Nukleus Pulposus Servikalis Cervical Herniated Nucleus Pulposus. Jurnal Lampung Medical Faculty, 6.
Moore, K. L.; Dalley, A. F.; Agur, A. M. R. (2014). Moore Clinically Oriented Anatomy Seventh Edition. In Wolters Kluwer (Vol. 282, Issue 15).
Nahadewa, T. G. B. (2013). Saraf Perifer. PT. Indeks, 1–61.<!--[if supportFields]>ADDIN Mendeley Bibliography CSL_BIBLIOGRAPHY <![endif]-->
Panduwinata, W. (2014). Peranan Magnetic Resonance Imaging dalam Diagnosis Nyeri Punggung Bawah Kronik. Cdk, 41(4).
Ren, A. J., Guo, Y., Tian, S. P., Shi, L. J., & Huang, M. H. (2012). MR imaging of the spine at
Wang, Q., Li, H., Kong, J., Li, X., Feng, L., & Wu, Z. (2021). Diagnostic agreement between 3.0-T MRI sequences of nerve root and surgery in patients with cervical radiculopathy A retrospective study. Medicine (United States), 100(4), 0–5. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000024207
Wassenaar, M., Van Rijn, R. M., Van Tulder, M. W., Verhagen, A. P., Van Der Windt, D. A. W. M., Koes, B. W., De Boer, M. R., Ginai, A. Z., & Ostelo, R. W. J. G. (2012). Magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosing lumbar spinal pathology in adult patients with low back pain or sciatica: A diagnostic systematic review. European Spine Journal, 21(2), 220–227. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-011-2019-8
Westbrook, C., & Talbot, J. (2019). MRI in Practice Fifth Edition. In Acta Universitatis Agriculturae et Silviculturae Mendelianae Brunensis (Vol. 53, Issue 9).
Sumber gambar: Dokumentasi Humas RSO
<!--[if supportFields]><![endif]-->